No products in the cart.
VPS is a popular service that allows users to set up their own virtual machines without paying for full bare metal server capacity. Studying the technology behind a VPS is a good start to understanding the cloud as a whole, as VPS instances are basically the building blocks of any cloud. Most cloud users are somewhat familiar with the terms VPS, virtual machine, or compute instance, but few understand the service on a technical level. This article explains everything about VPS and how does VPS work?
What does VPS stand for?
VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. A VPS is a virtual environment that runs on a physical server, usually somewhere in a data center. Thanks to a technology called virtualization, a VPS behaves like a virtual computer with its own virtual CPU cores, RAM, storage, and network interfaces.
Virtualization. The technology behind VPS
What is virtualization?
As mentioned above, the process of creating a virtual operating system on a physical server is called virtualization. On a single physical computer, multiple users can run different operating systems, all independent of each other. For example, user A can use CentOS, while user B uses Debian on a virtual machine on the same physical server.
hypervisor
A hypervisor is software that supports virtualization. It connects directly to the server hardware and allocates resources like RAM and CPU to each VPS. While from the user’s perspective each virtual machine is a fully functional environment, from the provider’s perspective it is just a single data file that can be moved around as needed.
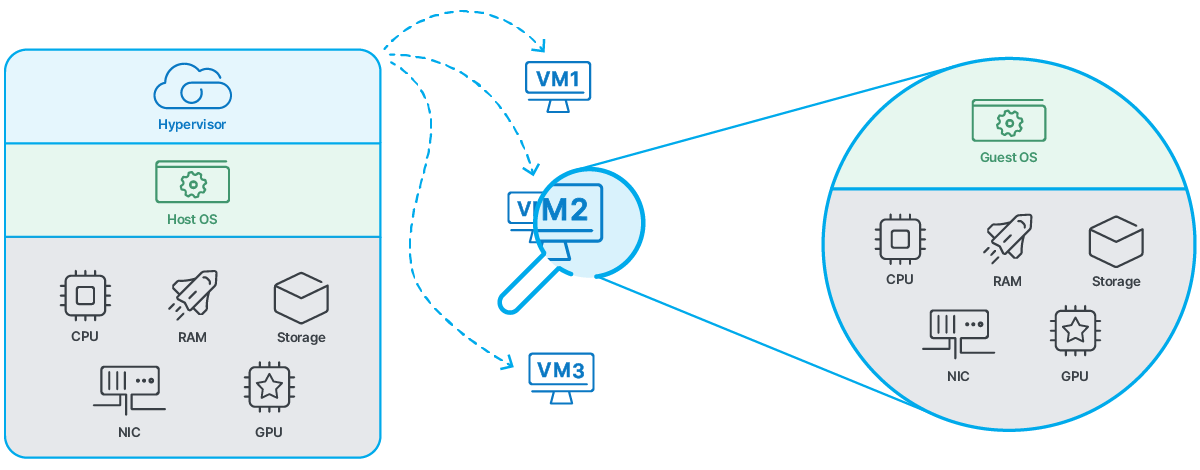
Example of virtualization using a hypervisor. Several virtual instances are created (VM1, 2, 3) – all of them share the same hardware capacity.
Key Advantages of VPS
independence and safety
One of the main advantages of a VPS is that instances often have root access, so they have unlimited access to change the operating system. Install and run applications and packages.
Not only does it allow a high level of customization for each VPS, but it also ensures complete separation between each environment. If one of the VPS becomes unresponsive or hacked, the other VPS will not be affected. This independence is very beneficial in reducing risk – if one element fails, the rest of the environment remains intact. This also makes a VPS the perfect sandbox for developing and testing new things.
“If one of the VPS instances becomes unresponsive or gets hacked, the others will remain unaffected”
Customization and Affordability
The rise of VPSs has also contributed to the growing popularity of microservices. With dedicated servers, the approach of deploying 1 server = 1 task is expensive because most of the server capacity will be wasted. But VPS is much cheaper because you can create a small instance with resources just for this one task. Another reason is the portability and scalability of virtual machines, which are discussed below.
Portability and Extensibility
From a vendor’s perspective, each VPS is a large data file that runs on the host system, thanks to a hypervisor. This large data file can be moved to another server. This makes it possible to move a VPS from one physical host to another without stopping the machine.
Since the VPS operating system is virtual, it is very easy to scale up or down the instance. In other words, if you run out of hardware capacity, you can always buy more. For Holland WEB, just send us a message to [email protected]. Tell us how much you want to increase CPU cores, RAM or disk capacity.
“The VPS is a slice of a dedicated server for a fraction of the cost”
VPS vs Virtual Dedicated Server
Like VPS, Virtual Dedicated Server is a virtual machine. However, VDS allocates more computing power, using both virtual and dedicated resources. The CPU and memory of a VDS are not shared, similar to a dedicated server. VDS is a great solution for users who need the portability of a VPS and the power of a dedicated server.
VPS vs Shared Web Hosting
Some people compare VPS to shared web hosting. While both can be used to host a website or webmail, shared hosting does not provide root access and the ability to run any application you want. If your website performance is constantly suffering from high traffic and your clients are complaining about slow website speeds, it’s time to switch to a VPS.




 Web Hosting
Web Hosting Web Designs
Web Designs Graphic Design
Graphic Design SEO
SEO Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing