No products in the cart.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of optimizing your website to rank higher on search engine result pages (SERPs) and improve its visibility and traffic. SEO is essential for businesses of all sizes to get found online and reach their target audience. In this ultimate guide to SEO, we’ll cover everything you need to know to get started with SEO and improve your website’s search engine ranking.
Keyword Research
Finding the keywords and phrases that your target audience is searching for online is a critical step in optimizing your online presence, whether it’s for a website, a blog, or an e-commerce store. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do this:
Understand Your Target Audience:
Before you start searching for keywords, you need a clear understanding of your target audience. Who are they? What are their demographics, interests, and pain points? Knowing your audience will help you create content that appeals to them.
Brainstorm Seed Keywords:
Start with a list of general, broad keywords related to your niche or industry. These are your seed keywords. For example, if you have a fitness blog, seed keywords could include “weight loss,” “muscle building,” or “healthy eating.”
Use Keyword Research Tools:
There are several keyword research tools available that can help you identify keywords and phrases. Some popular options include:
Google Keyword Planner:
This is a free tool that provides keyword suggestions and data on search volume.
SEMrush:
A paid tool that offers comprehensive keyword data.
Ahrefs:
Another paid tool known for its detailed keyword research capabilities.
Ubersuggest:
A free tool that provides keyword ideas and SEO metrics.
Analyze Competitors:
Look at your competitors’ websites and content to see what keywords they are targeting. Tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs can help you identify the keywords that your competitors are ranking for.
Long-Tail Keywords:
Long-tail keywords are specific, longer phrases that users might search for. They often have less competition and can bring more targeted traffic. Include long-tail keywords in your strategy.
Check Search Volume and Competition:
In your chosen keyword research tool, look at the search volume and competition for each keyword. You want to find keywords with a reasonable search volume and manageable competition.
Consider User Intent:
Focus on keywords that match the intent of your target audience. Are they looking for information, product reviews, or ready to make a purchase? Tailor your content accordingly.
Create a Keyword List:
Organize your chosen keywords into a list. You can use spreadsheets or tools like Google Sheets to keep track of them.
Local SEO
(if applicable): If you have a local business, don’t forget to include location-based keywords to attract local customers. For example, “best Italian restaurant in [your city].”
User Feedback:
Listen to your audience’s feedback and questions. These can provide insights into what they are searching for and help you identify new keywords and content ideas.
On-Page Optimization
Title Tag:
Include your target keyword in the title tag, preferably near the beginning. Keep the title informative and engaging. (Recommended: 35 – 60 characters).
Meta Description:
Craft a compelling meta description that includes the keyword. Make it concise and relevant to encourage clicks. (Recommended: 140 – 160 characters).
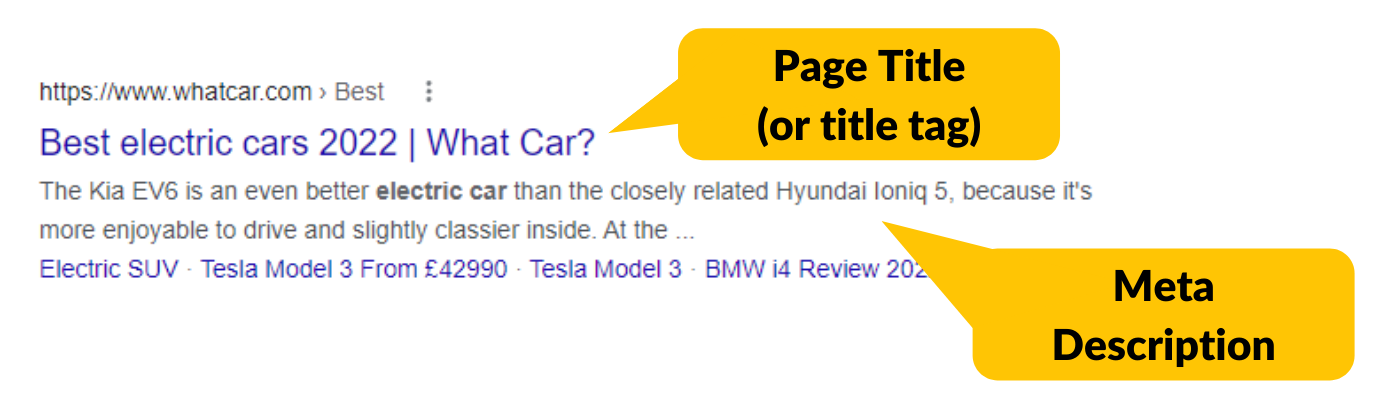
Header Tags:
Use header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to structure your content. Include your target keyword in at least one of these header tags. and It is generally recommended to use one H1 tag per page, and then use H2, H3, etc. tags for subheadings. This helps to create a clear hierarchy of information on the page, making it easier for users to understand and navigate. However, it’s important to note that there is no hard and fast rule for how many heading tags to use, as it can vary depending on the content and design of the page. The most important thing is to use them in a logical and meaningful way that helps to organize and structure your content.
Keyword Placement:
Naturally, incorporate the target keyword throughout the content, but avoid keyword stuffing. Include it in the first paragraph, headings, and throughout the body.
Content Quality:
Create high-quality, informative, and engaging content. The longer, comprehensive content often performs better.
Internal Links:
Include internal links to other relevant pages on your website to improve user engagement and navigation.
External Links:
When appropriate, Link to authoritative, relevant external sources to back up your content.
Image Optimization:
Optimize images by including descriptive alt text and compressing them for faster loading times.
Off-Page Optimization
Off-page optimization, also known as off-page SEO, involves strategies and techniques that you implement outside of your website to improve its search engine ranking and online visibility. Off-page SEO is crucial for building your website’s authority and credibility in the eyes of search engines. Here are some key strategies for off-page optimization:
Link Building:
- Building high-quality backlinks is one of the most important aspects of off-page SEO. Quality matters more than quantity. Focus on obtaining backlinks from authoritative and relevant websites in your niche.
- Strategies for link building include guest posting, creating valuable and shareable content, broken link building, and reaching out to industry influencers for link opportunities.
- Avoid spammy link-building practices, as these can lead to penalties from search engines.
Social Media Engagement:
- Actively engage on social media platforms to promote your content and build your brand’s online presence. Share your content, interact with your audience, and encourage social sharing.
- Social signals (such as likes, shares, and comments) can indirectly impact your SEO rankings by increasing your website’s visibility and authority.
Content Marketing:
- Create high-quality, shareable content that naturally attracts backlinks. Infographics, videos, blog posts, and guides can be effective forms of content.
- Promote your content through various channels, such as social media, email marketing, and content syndication platforms.
Influencer Outreach:
- Connect with influencers and authoritative figures in your industry. Building relationships with these individuals can lead to opportunities for guest posting and endorsements.
Online Reviews:
- Encourage and manage online reviews, especially on platforms like Google My Business and industry-specific review sites. Positive reviews can improve your local and organic search rankings.
Local SEO:
- If your business serves a local audience, optimize for local search. Create and optimize your Google My Business listing, and ensure your NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) information is consistent across all online directories.
Community Engagement:
- Actively participate in online forums, discussion boards, and relevant online communities. This can help you establish yourself as an authority and drive traffic to your website through your profile and links in your posts.
Brand Mentions:
- Monitor mentions of your brand or website on the web. Reach out to those who mention you but haven’t linked to your site and request a link when appropriate.
PR and Outreach:
- Share news and noteworthy events related to your business. Press releases and outreach to relevant news outlets can help you earn valuable mentions and links.
Social Bookmarking:
- Share your content on social bookmarking sites like Reddit, Digg, and StumbleUpon, but avoid spammy practices.
Document Sharing:
- Share documents, presentations, and PDFs related to your niche on document sharing platforms like SlideShare and Scribd. Include links back to your website.
Video Marketing:
- Create and optimize videos for platforms like YouTube. Video content can help you reach a broader audience and drive traffic back to your site.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is a critical aspect of optimizing your website for search engines and ensuring that it’s accessible, indexable, and performs well. Here are the best practices for performing technical SEO on your website:
Optimize Website Speed:
- Page speed is a significant ranking factor. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to identify performance issues.
- Compress images and other media files to reduce their size.
- Minimize HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files.
- Leverage browser caching and implement Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to improve loading times.
Mobile Optimization:
- Ensure your website is mobile responsive and provides a good user experience on all devices. Google uses mobile-first indexing.
- Test your website’s mobile-friendliness with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
Crawlability and Indexability:
- Create a sitemap (XML and HTML) and submit it to Google Search Console.
- Use a robots.txt file to control which parts of your site search engine bots can access.
- Check for crawl errors and issues in Google Search Console and address them.
- Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of duplicate or similar content.
URL Structure:
- Use descriptive, readable URLs that include relevant keywords.
- Avoid long, complex, and dynamically generated URLs.
- Implement a consistent URL structure and hierarchy.
SSL/HTTPS:
- Secure your website with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to provide a secure connection (HTTPS). Google gives preference to secure sites.
Structured Data Markup:
- Implement structured data markup (Schema.org) to provide context to search engines, which can lead to rich snippets in search results.
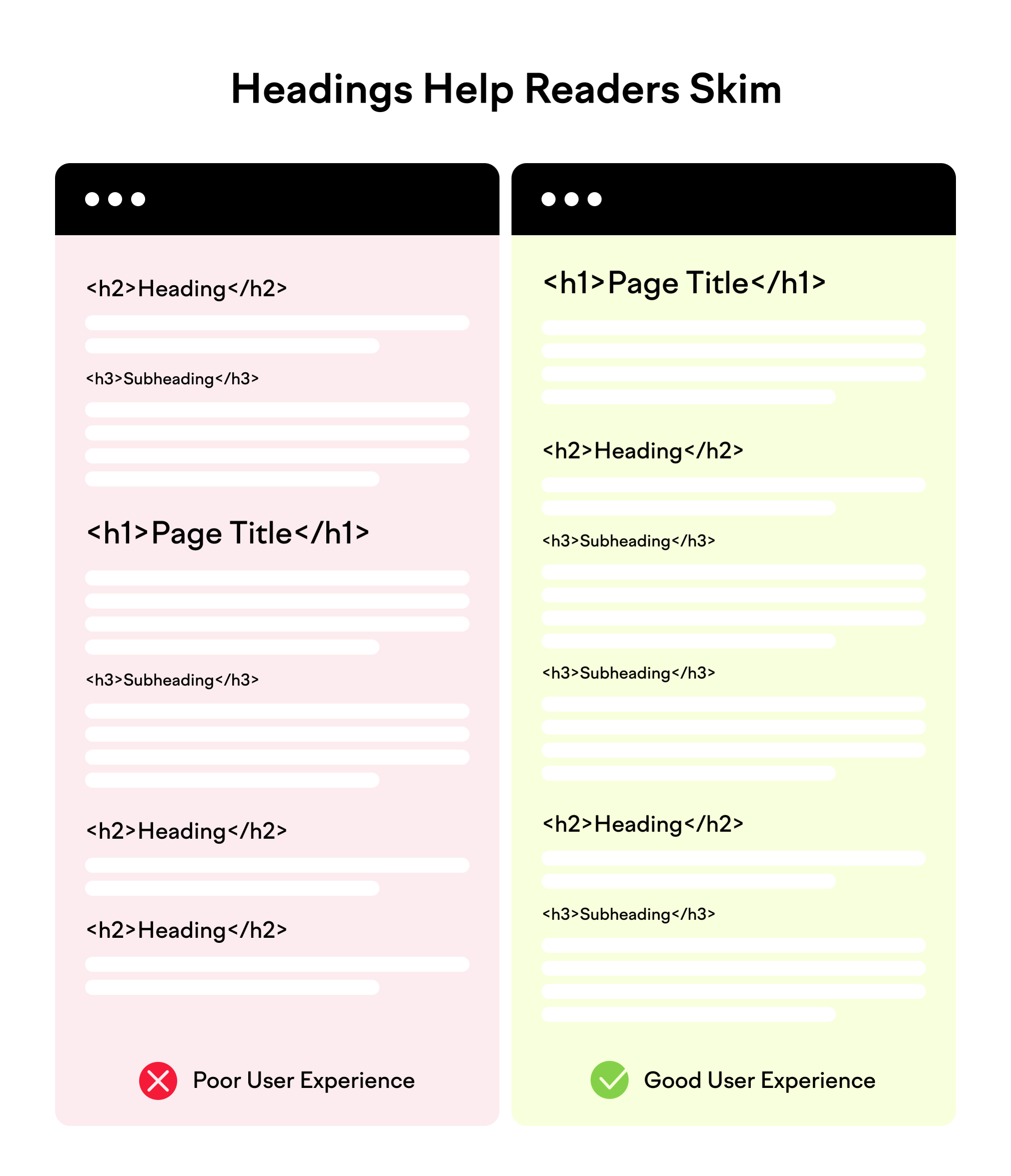
Heading Tags:
- Use proper header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to structure your content. Make sure they follow a logical hierarchy.
Image Optimization:
- Use descriptive and keyword-rich alt tags for images to improve accessibility and SEO.
- Compress and optimize images to reduce file sizes and improve loading times.
XML Sitemaps:
- Create XML sitemaps to help search engines index your site efficiently. Submit them to Google and other search engines.
Pagination and Canonicalization:
- Properly handle pagination, especially on e-commerce sites, using rel=”prev” and rel=”next” tags.
- Implement canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues.
404 Error Handling:
- Create a custom 404 error page to improve the user experience when visitors land on non-existent pages.
- Regularly monitor and fix broken links on your website.
Internal Linking:
- Implement a logical internal linking structure to guide users and search engines through your site’s content.
- Include relevant anchor text in your internal links.
HTTP to HTTPS Migration:
- If you transition from HTTP to HTTPS, ensure proper redirection using 301 redirects and update all internal and external links.
Site Architecture:
- Create a logical, user-friendly site structure with a clear hierarchy. Use breadcrumbs to aid navigation.
Mobile AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages):
- Consider implementing AMP for your mobile content to enhance the mobile user experience and potentially improve rankings.
Security and Updates:
- Keep your website’s content management system (CMS) and plugins up to date to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Implement security measures to protect your site from hackers and malware.
Performance and Analytics:
- Continuously monitor your site’s performance using tools like Google Analytics to identify issues and track the impact of your changes.
Local SEO
Local SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a digital marketing strategy focused on improving a website’s visibility in local search results. It aims to help businesses attract more local customers by optimizing their online presence for location-based queries. Key components of local SEO include optimizing Google My Business, Bing Places for Business, and other online directories, managing online reviews, creating locally relevant content, and ensuring consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) information across online directories. Local SEO is crucial for brick-and-mortar businesses and service providers seeking to increase their online and in-store visibility among local audiences.
Content Marketing
Content marketing can significantly improve your website’s search engine ranking by creating high-quality, relevant, and valuable content that attracts both users and search engines. Here’s how content marketing can help:
Quality Content:
Creating informative, well-researched, and engaging content can position your website as an authoritative resource in your niche. Search engines tend to reward websites that consistently provide valuable content.
How I will get quality content?
- Hiring in-house content creators, such as writers, editors, and graphic designers.
- Freelance writers specialize in various niches, such as: Upwork, Freelancer, and Fiverr.
- Websites like Contently and Skyword connect businesses with professional content creators and journalists.
- Platforms like HubSpot, MarketMuse, and ClearVoice offer content creation and marketing services.
- Collaborate with universities or experts in your field to develop authoritative content.
- You can find high-quality, free-to-use content in the public domain like Wikimedia Commons, Pixabay, and Unsplash.
Content length
The content length represents the number of words found on the webpage. The webpage should contain a decent amount of words. Depending on the topic’s complexity and your goals, the recommended range for content length and density is quite broad, from a minimum of 200 to a maximum of 1,000 words per page. The primary objective of website content is to convey the intended message and motivate the reader to take the desired action in as few words as possible.
Text-to-HTML ratio
The starting point for a good text-to-code ratio is 10%. If your page’s content-to-code ratio is under 10%, you should either improve your HTML, CSS, and JS, or add more content.
However, you shouldn’t take the rule of thumb of a 10% ratio too seriously. After all, your site is your baby, so design it however you see fit.
In fact, any ratio between 25% and 70% text to HTML is considered optimal. You may have noticed that many of the websites that rank highly in search results also feature noticeable text. This is especially true since the release of the Panda update by Google and other search engines, which prioritised content based sites.
Keyword Optimization:
By strategically incorporating relevant keywords into your content, you can improve your website’s visibility in search results. As we mentioned above 👆🏻, Targeting both short-tail and long-tail keywords in your content helps capture a broader range of search queries.
Backlinks:
High-quality content tends to attract backlinks from other websites. When authoritative websites link to your content, it signals to search engines that your content is valuable. This can lead to higher search engine rankings.
User Engagement:
Content that engages and retains users on your site for longer durations sends positive signals to search engines. It can reduce your site’s bounce rate and improve your ranking.
Freshness:
Regularly updating and adding new content to your website keeps it fresh and relevant. Search engines often favor fresh content, particularly for news topics or areas where recent information is important.
Structured Data and Rich Snippets:
By implementing structured data (Schema markup), you can provide additional context to search engines, leading to enhanced and eye-catching search result snippets, which can improve click through rates.
Internal Linking:
Content marketing allows you to naturally create internal links, which improve the navigation of your site and distribute link equity to important pages.
Social Signals:
Sharing your content on social media platforms can increase its visibility and reach a broader audience. While social signals are not a direct ranking factor, they can indirectly impact your website’s search engine rankings.
Long-Term Benefits:
Quality content provides long-term benefits. Once you’ve created evergreen content, it can continue to attract traffic and backlinks over time, improving your site’s authority and rankings.
Brand Building:
Consistent content marketing can help build brand authority and recognition, which can indirectly impact search engine rankings. A recognizable brand is more likely to get clicks and engagement.
User Intent Matching:
Effective content marketing aligns with user intent. This means your content answers questions and provides solutions that people are looking for, which is a positive ranking factor.
Reducing Duplicate Content:
By producing original, valuable content, you reduce the risk of duplicate content issues that can negatively affect SEO.
Analytics and Tracking
Analytics and tracking are essential for monitoring and improving your website’s search engine ranking. You can use tools like Google Analytics or Piwik to track your website’s traffic, bounce rate, and conversion rate. Additionally, you should implement conversion tracking to monitor the actions of your site’s visitors. Such as filling out a contact form or making a purchase. We have prepared for you Google Analytics Dashboard Guideline.
In conclusion
SEO is an essential part of any digital marketing strategy. By optimizing your website’s content, on-page and off-page elements, technical elements, and local search engine ranking. You can improve your website’s search engine ranking and attract more relevant traffic to your website. By creating valuable, relevant, and informative content and tracking your website’s performance, you can continue to improve your website search engine ranking and achieve your digital marketing goals.



 Web Hosting
Web Hosting Web Designs
Web Designs Graphic Design
Graphic Design SEO
SEO Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing